The tar command stands for tape archive and it is used for backup purpose. It is very useful command that one need to know when it comes to personal data and so on. In this article, check out this 10 very useful and practical tar command examples.
1. Create a tar archive
In this example, we are going to create tar archive. Here's the command.
Once this command is executed, it will create bhlarchive.tar file. In above example we have:- c which will create a new tar archive
- v verbose (show me what you are doing)
- f archive tape
2. Show content of tar archive
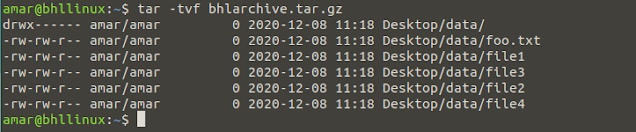
If we want to show the content of tar archive without extracting it, we can use the following command.
As we can see on the above image, the output of previously created archive has been shown in terminal. That lover t in the above command is used to show the archive content. 3. Untar the tar archive
In case we want to extract the previously created archive, we can use the following command.
As we see, the command has extracted all the content of bhlarchive.tar into the BHL_ARCHIVE directory which is located on Desktop. Note: The -x will extract the archive while -C is used to specify destination directory in which we are extraction the archive. 4. Create tar.gz archive
In order to create gzip archive, we can use the following command.
In the above command, we have use -z flag to make a gzip archive file. 5. Create tar.bz2 archive
The bz2 feature compress and create archive file less than the size of gzip. In order to make a bz2 archive, we can use the following command.
In the above command -j flag represents the bz2 archive file.
6. Show the content of tar.bz2 archive
In order to show the content of tar.bz2 archive, we can use the following command.
7. Uncompress tar.bz2 archiveIn order to uncompress the content of tar.bz2 archive, we can use the following command.
In above command I have used -C flag to extract the content of bhlarchive.tar.bz2 into myBZ2archive directory. 8. Show the content of tar.gz archive
In order to show the content of tar.gz archive, we can use the following command.
9. Extract tar.gz archive In order to extract the content of the tar.gz archive, we can use the following command.
In above command, once again I have used -C flag to extract the content of the bhlarchive.tar.gz archive into myGZarchive directory.10. Untar single file from tar archive
In order to untar single file from tar archive, we can use the following command.
In above example, I have used -C flag to extract only '7.png' file from bhlarchive.tar into a /tmp/data directory. Conclusion
Working with tar is very useful and once you master it, you can use it to make a backup of your files and prevent data loss or damage. In this article, I have successfully shown you how to make a tar archive, how to view it's content, how to extract it. This article has also shown how to make tar.gz, tar.bz archive and how to extract a full archive into specific directory or untar single file into desired directory. If you like this article, make sure to share it, leave a comment down bellow in case you have notice any technical error in this article. I see you next time.